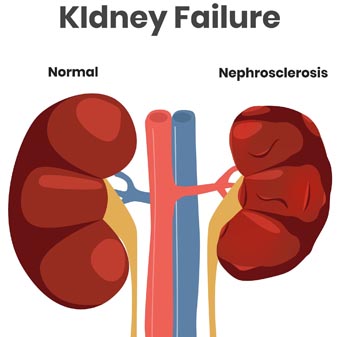
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure, is a medical condition in which the kidneys are unable to adequately filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall health by removing waste products, regulating electrolyte balance, and controlling blood pressure. When the kidneys fail, these essential functions are compromised, leading to a buildup of waste and fluid in the body.
Patients with kidney failure presents with wide variety of symptoms like increased :
- - night time urination
- - decreased urination
- - swelling
- - loss of appetite
- - nausea, vomiting
- - fatigue
- - shortness of breath, or
- - unexplained anemia.
How is kidney failure diagnosed?
A healthcare provider may use a variety of kidney function tests to evaluate your kidneys and diagnose kidney failure. If the provider suspects you’re at risk of kidney failure, common tests include:
Blood Tests Blood tests show how well your kidneys remove waste from your blood. A provider will use a thin needle to withdraw a small amount of blood from a vein in your arm. Technicians will then analyze your blood sample at a lab.
Urine Tests Urine tests measure specific substances in your pee, such as protein or blood. You’ll pee into a special container at a provider’s office or a hospital. Technicians will then analyze your urine sample at a lab.
Imaging Tests Imaging tests allow a provider to look at your kidneys and the surrounding areas to identify abnormalities or blockages. Common imaging tests include kidney ultrasound, CT urogram and MRI.
How is kidney failure treated?
Kidney failure treatment depends on the cause and extent of the problem. There are two main treatments for kidney failure.
Dialysis
Dialysis helps your body filter blood. There are two types of dialysis:
Hemodialysis In hemodialysis, a machine regularly cleans your blood for you. Most people get hemodialysis three to four days a week at a hospital or dialysis clinic.
Peritoneal dialysis In peritoneal dialysis, a provider attaches a bag with a dialysis solution to a catheter in your abdominal lining. The solution flows from the bag into your abdominal lining, absorbs waste products and extra fluids and drains back into the bag. Sometimes people can receive peritoneal dialysis at home.
Kidney transplant
A surgeon places a healthy kidney in your body during a kidney transplant to take over for your damaged kidney. The healthy kidney (donor organ) may come from a deceased donor or a living donor. You can live well with one healthy kidney.
