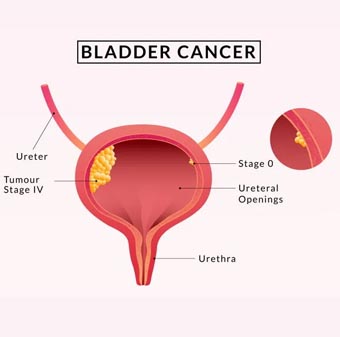
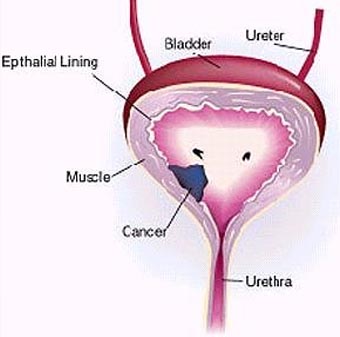
Bladder Cancer refers to cancer that arises in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated in the lower abdomen and stores urine. Bladder cancer is one of the most common types of cancer seen in men.
Bladder Cancer generally begins in the urothelial cells. These cells are lined inside the bladder. The Urothelial Cells can even be found in the Kidneys and Ureters (the tube that connects the bladder and the kidneys). There is a chance for urothelial cancer to occur in the kidneys and ureters, however, this type of cancer is more common in the bladder.
Most bladder cancers are diagnosed during the stage when the cancer is completely treatable. However, there have been certain instances where early-stage bladder cancer relapsed even after successful treatment. Therefore, people need to go for regular follow-up tests for years after their treatment for the prevention of a relapse.
Common signs and symptoms of bladder cancer are:
- - Blood in the Urine (Hematuria) or blood clot in the urine
- - Burning or painful sensation during urination
- - Having the constant need to urinate frequently
- - Having the urge to urinate but being unable to do so
- - Back pain on 1 side of the lower body
How is this cancer treated?
Just like other cancers bladder cancer also develops in stages. However, it is mostly identified in the early stages. Different stages require different treatments. Depending upon your stage of cancer one or more of the following treatments is provided at our centre.
Surgery to completely remove the cancer cells
Chemotherapy in the bladder, to treat cancers confined to the lining of the bladder but have a high risk of recurrence or progression to a higher stage
Chemotherapy for the whole body when cells can’t be removed.
Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells, often used as a primary treatment when surgery isn't an option or isn't desired.
Immunotherapy triggers the body's immune system to fight cancer cells, either in the bladder or throughout the body.
Targeted therapy to treat advanced cancer when other treatments haven't helped
Bladder cancer can reoccur or may develop a cancerous cell elsewhere in the body. It is better to follow up with the treating doctor at regular intervals.
